python
一、Overview
1.1 First Program
print("hello world!")
1.2 Variables
# 1. var
num = 12
num: int = 20
# init
x: int
x = 12
# 2. multi-var
x, y = 3, 7.2
memory address
num = 12
print(id(num)) # 4335862352
num = 10
print(id(num)) # 4335862288
1.3 Data Types
# number
num : int = 7
pi : float = 3.14
c : complex = 1 + 2j
# boolean
flag: bool = True
# string
name: str = "John Smith"
# core type
nums: list = [1, 2, 3]
tup : tuple = ('a', "bc", 123)
d : dict = {"name": "John Smith", "age": 27, "sex": 1}
s : set = {1, 3, "ab"}
# null
None
is not None
1.4 Input & Output
input
a = input() # string
a = int(input()) # int
a,b = input().split() # 输入两个字符串
a,b = map(int, input().split()) # 输入两个整数(用空格隔开)
a,b = map(int, input().split(',')) # 输入两个整数(用逗号隔开)
# tips
a = input("please enter a string: ") # str
output
print()
print(string%...)
print(string.format(var...))
print(f-string)
for example
num: float = 12.963
# 保留两位小数
print('%.2f'%num)
print('{0:.2f}'.format(num))
print(f'{num}')
print("{x}, {y}".format(x = 2, y = 12))
1.5 Comments
# this is a single line comment
'''
this is a multi-line comment
'''
def func():
"""
multiple comment
"""
# code
1.6 Operators
+ - * / % `//` `**`
== != >= <= > <
+= -= *= /= %=
`and or not`
`i += 1 i -= 1`
`s = "pass" if score > 60 else "fail"`
for example
print( 10 / 2 ) # 5.0
print( 10 // 2 ) # 5
print( 3 ** 2 ) # 9
print( "Hello" * 2 ) # HelloHello
print( "hello" + " world" ) # "hello world"
1.7 import
import ... [as ...]
from ... import ... [as ...]
$ pip install library_name
1.8 Main
if __name__ = "__main__":
print("this py file is not be import!")
1.9 Package exe
cmd> pyinstaller -F -w *.pyw
二、Control Structures
If statement
if condition:
# statement(s)
elif condition:
# statement(s)
elif condition:
# statement(s)
else:
# statement(s)
For Loop
nums = [1, 3, 6, 2, 4]
for i in range(len(nums)):
# statement(s)
for v in nums:
# statement(s)
for i, v in enumerate(nums):
# statement(s)
While Loop
while condition:
# statement(s)
break & continue
三、常用数据类型
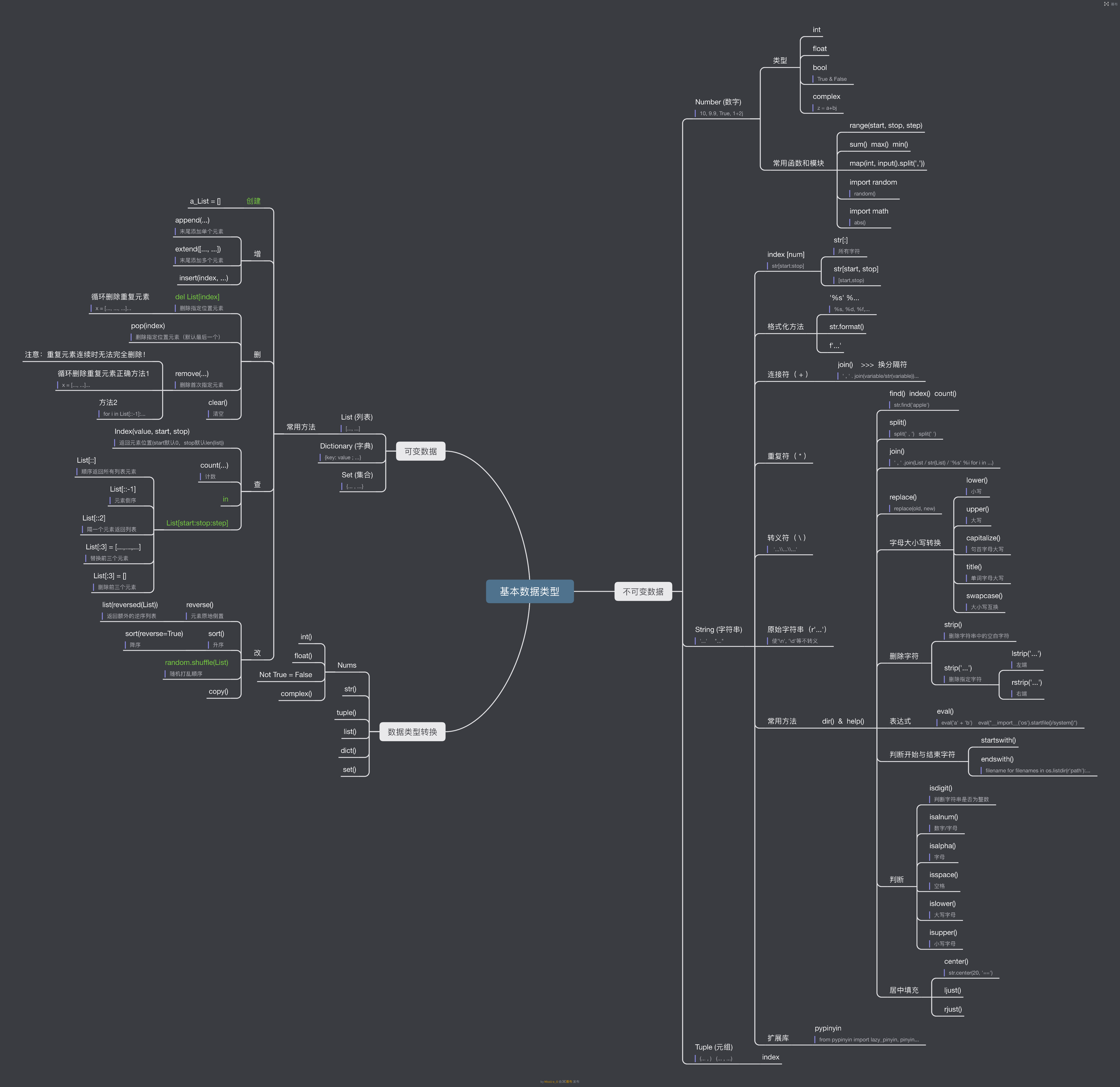
1. Number
- int
- float
- complex
a: int = 12
b: float = 12.5
c: complex = 1 + 2j
2. Boolean
flag: bool = True
flag: bool = False
3. String
s = "hello world"
s: str = "hello world"
s = """this
is a multi-line
text"""
# 查
.find(str) | .rfind(str) # (不存在返回-1)
.index(str) # (不存在则抛出异常)
.count(str) # (不存在返回0)
s[i]
# string-list 转换
.split() # 默认为任意空白字符(space, \n,\t...)
''.join(nums)
# 改
.replace(old, new)
.strip() # 删除两端空白字符
# 反转字符串
s[::-1]
# 大小写:
.upper()
.lower()
.capitalize() # 字符串首字母大写
.title() # 字符串每个单词首字母大写
.swapcase() # 大小写转换
# 判断:
.startswith()
.endswith()
.isalpha()
.isdigit()
.isalnum() # 字符或数字
.isupper()
.islower()
.isspace()
# 填充:
.center()
.ljust()
.rjust()
eval(s) # 表达式求值
translate(''.maketrans()) # 加密
for i in s:
# code
4. 列表 List
不限制元素类型是否相同
元素值可重复!
nums = [3, 1, 7, 12, 6]
nums: list = [3, 1, 7, 12, 6]
# notice !
things = ["string", 0, [1, 2, 3], 3.14, num]
# 增
.append(e) # 末尾新增元素
.insert(i, e) # 中间插入元素
.extend([1, 2]) # 末尾合并新的列表元素(原地址)
+= [1, 2] # 末尾合并新的列表元素
# 删
.pop() # 末尾删除元素
.pop(i) # 删除指定index的value(index越界会报错)
.remove(e) # 删除指定单个value (value不存在则报错)
.clear() # 清空元素
del nums[i] # 删除指定index的value(index越界会报错)
del nums[l:r] # 删除指定范围内[l, r)的元素
del nums[:] # 清空元素
# 查
len(nums) # 长度
.index(e) # 元素值的索引 (不存在该元素值则ValueError: 2 is not in list)
.count(e) # 元素值出现的次数
.copy() # 浅复制
if x in nums: # 包含
if x not in nums: # 判断不包含(可读性强)
# 改
nums[i] = x # 修改指定index的value
# 排序
.sort() # 升序
.sort(reverse=True) # 降序
.sort(key=None, reverse=False) # 默认升序
.reverse() # 反转
random.shuffle(nums) # 随机顺序, 需引入 import random
# 排序并返回新列表,原列表不变
sorted(nums) # 升序
sorted(nums, reverse=True) # 降序
reversed(nums)
len(nums) # 长度
id(nums) # 内存地址
sum(nums)
max(nums)
min(nums)
for i in range(len(nums)):
# code
for i in nums:
# print(i)
for i, v in enumerate(nums):
# print(i, v)
# 切片[start:stop:step]
List[::] # 顺序返回所有列表元素
List[::-1] # 倒序返回所有列表元素
List[::2] # 每隔1个元素提取到列表
List[:3] # 前三个元素
List[3:]
List[i] # 访问元素
del List[i] # 删除元素
List[i] = x # 修改元素
# 删除有序数组的重复项(末尾删除)
for i in range(len(nums)-1, -1, -1):
if nums[i] == target:
nums.remove(nums[i])
for i in List[::-1]:
if List[i] == x:
del nums[i]
5. 元组 Tuple
元组与列表类似,不同之处在于元组的元素不能修改。
tup = ('Google', 'Runoob', 1997, 2000)
tup = (1, 2, 3, 4, 5)
tup = (50,) # 只包含一个元素时, 需添加逗号(不加逗号,类型为整型)
6. 字典 dict
d = {}
d = dict()
d = {
'name': 'john',
'age': 23,
'email': 'john@163.com'
}
# 查
d[k]
.get(k, default=None)
.keys()
.values()
.items()
# 增
d[k] = value
.update({'sex': 'male'})
# 删
.pop(k)
.clear()
# 判断
if k in d:
# 按key排序
sorted(d)
# 按value降序
sorted(d.items(), key = lambda x: -x[1])
# 先按名称排序,同名则按年龄降序:
sorted(d.items(), key = lambda x:(x['name'], -x['age']))
# 效果:{'a': 87, 'b': 78, 'c': 98, 'd': 67}
# 代码:
x = ['a','b','c','d']
y = [87, 78, 98, 67]
print({i:j for i,j in zip(x,y)})
# 字典统计
d = {}
for num in nums:
d[num] = d.get(num, 0) + 1
7. 集合 Set
se = {}
se = {3, 1, 6, 2}
se = set({3, 1, 6, 2})
print(se) # {1, 2, 3, 6} 自动排序
.add(x) # 末尾添加
.pop() # 头部删除
.remove(x)
.clear()
# A∪B、A∩B、差集、对称差集:| & - ^
# 子集:< >
四、Function
def hello():
# code
def hello(name, age):
# code
def hello(name = "John Smith"):
# code
def hello(name):
return "hello " + name
def square(x):
return x * x
def test(func, x):
print(func(x))
def polynomial(x):
return x ** 2 + 5
print(polynomial(2)) # 9
print((lambda x: x ** 2 + 5)(2)) # 9
mult = lambda x: x * x
print(mult(3)) # 9
str(12) # '12'
id() # 返回变量值的内存地址
range(5) # [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
range(1, 5) # [1, 2, 3, 4]
range(1, 5, 2) # [1, 3]
五、pythonic编程技巧
创建时间:2021年4月22日,更新时间:2021年8月27日
import this # python之禅
1. 变量的交换
# other
tmp = a
a = b
b = tmp
# python
a, b = b, a
2. 字符串格式化
#组合/拼接字符串
name = "Ross"
country = "China"
age = 28
print("Hi, I'm " + name + ". I'm from " + country + ". And I'm " + str(age) + ".")
# str%()
print("Hi, I'm %s. I'm from %s. And I'm %d." % (name, country, age))
# str.format()
print("Hi, I'm {}. I'm from {}. And I'm {}.".format(name, country, age))
print("Hi, I'm {0}. I'm from {1}. And I'm {2}.".format(name, country, age))
print("该商品价格为:{0:.2f}".format(price))
print(f"Hi, I'm {name}. I'm from {country}. And I'm {age}.")
# f-string
print(f"该商品价格为:{price+1:.2f}")
3. Yield 语法
# 列举斐波那契数列前n的和
def fibonacci(n):
a, b = 0, 1
# nums = []
for _ in range(n):
# nums.append(a) -->> yield a
yield a # 立即输出,无需等待加载完毕再输出(极大减少程序耗时)
a, b = b, a+b
# return nums
for i in fibonacci(10):
print(i)
4. 列表解析式
# 常规
files = ['a.py', 'b.docx', 'c.txt', 'm.py', 'uio.py', 'date.txt']
new_files = []
for f in files:
if f.endswith('py'):
new_files.append(f)
#------------------------------------------------------------------
files = ['a.py', 'b.docx', 'c.txt', 'm.py', 'uio.py', 'date.txt']
# python
new_files = [x for x in files if x.endswith('py')]
5. Enumerate 函数
files = ['a.py', 'b.docx', 'c.txt', 'm.py', 'uio.py', 'date.txt']
# for i in files:
# print(i)
for i, x in enumerate(files): # (i)索引,(x)内容
print(i, x)
'''
0 a.py
1 b.docx
2 c.txt
3 m.py
4 uio.py
5 date.txt
'''
# 5.1 反向遍历(Looping Backwards)
files = ['a.py', 'b.docx', 'c.txt', 'm.py', 'uio.py', 'date.txt']
for i, x in enumerate(reversed(files)):
print(i, x)
# 5.2 按顺序排序(Looping in Sorted Order)
files = ['a.py', 'b.docx', 'c.txt', 'm.py', 'uio.py', 'date.txt']
for i, x in enumerate(sorted(files)):
print(i, x)
6. 字典的合并操作
a = {"coulson": "123456", "shville": "abc123"}
b = {"tom": "123", "john": "12345"}
c = {}
for k in a:
c[k] = a[k]
for k in b:
c[k] = b[k]
#-----------------------------------------------
c = {**a, **b} # 解包
7. 三元运算符
if score > 60:
s = "pass"
else:
s = "fail"
#-----------------
s = "pass" if score > 60 else "fail"
8. 序列解包
name = 'San Zhang'
str_list = name.split()
first_name = str_list[0]
last_name = str_list[1]
first_name, last_name = name.split()
9. With 语句
f = open("somefile.txt", "r")
s = f.read()
f.close()
# 如果忘记关闭这个文件,python会一直占用这个文件的系统资源,直到程序完全退出
#对于小脚本来说不是什么事,但对于一个需要长时间在服务器里运行的程序,系统资源可能很快就被吃光,然后程序崩溃
with open('somefile.txt','r') as f:
s=f.read() #with之后的语句执行完毕后文件会自动关闭,不用手动调用close()了
六、File
with open("test.txt", mode="r", encoding="utf8") as fp:
print(fp.read(5)) # 读取5个字符
print(fp.read()) # 读取全部字符
print(fp.readline()) # 读取一行
print(fp.readlines()) # 读取所有行,返回列表
# ['hello this is a text\n', 'you could change it\n', 'in here']
with open("test.txt", mode="w", encoding="utf8") as fp:
fp.write("hello this is a text\nyou could change it\nin here")
with open("test.txt", mode="a", encoding="utf8") as fp:
fp.write("hello this is a text\nyou could change it\nin here")
import os
# os.walk(): 更推荐
def walkDir(path) -> list:
# if not os.path.isdir(path):
# print('FileNotFoundError:', path, 'is not a directory or does not exist.')
# return
ans = []
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(path):
# for d in dirs:
# # print(os.path.join(root, d))
# # ans.append(os.path.join(root, d))
# pass
for f in files:
# print(os.path.join(root, f))
ans.append(os.path.join(root, f))
return ans
# os.listdir() 递归
def listDir(path):
for f in os.listdir(path):
fp = os.path.join(path, f)
print(fp) # dirs
if os.path.isdir(fp):
listDir(fp)
import os
def demo():
ans = []
for f in os.listdir(os.getcwd()):
if os.path.isfile(f) and f.endswith('.py'):
ans.append(f)
print(ans)
# ['get-filename.py', 'file.py', 'example-file.py', 'read-file.py']
packages
time
import time
# 当地时间
now = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
print(now)
# 休眠3秒
time.sleep(3)
# 统计用时
start = time.time()
end = time.time()
print(f'cpu执行用时: {(end - start) :.3f} s')
import calendar
cal = calendar.month(2021, 4)
print(cal)
'''
April 2021
Mo Tu We Th Fr Sa Su
1 2 3 4
5 6 7 8 9 10 11
12 13 14 15 16 17 18
19 20 21 22 23 24 25
26 27 28 29 30
'''
re
import re
s = "$1800, 卫衣, 90"
p = re.compile('\d+')
res = p.findall(s)
print(res)
# ['1800', '90']
random
# 1-100随机整数
random.randint(1, 100)
# 列表随机排序
random.shuffle(nums)
json
json.dumps(d)
json.loads(s)
mysql
import pymysql
conn = pymysql.connect(
host="127.0.0.1",
user="root",
password="root",
database="dbname",
charset="UTF8MB4"
)
cursor = conn.cursor()
sql = "SELECT * FROM user;"
cursor.execute(sql)
conn.commit()
import mysql.connector # pip install mysql-connector-python
db = mysql.connector.connect(
host="localhost",
port="3306",
user="root",
password="root",
database="sql_test"
)
cursor = db.cursor()
cursor.execute('''
CREATE TABLE if not exists customers (
id INT AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(255),
address VARCHAR(255)
);
''')
# 插入记录
sql = "INSERT INTO customers (name, address) VALUES (%s, %s)"
values = [("John Smith", "123 Main St"), ("Alice Johnson", "456 Elm St")]
cursor.executemany(sql, values)
db.commit()
# 查询记录
cursor.execute("SELECT * FROM customers")
results = cursor.fetchall()
for row in results:
print(row)
"""
# 更新记录
sql = "UPDATE customers SET address = %s WHERE name = %s"
values = ("789 Oak St", "Alice Johnson")
cursor.execute(sql, values)
db.commit()
# 删除记录
sql = "DELETE FROM customers WHERE name = %s"
values = ("John Smith",)
cursor.execute(sql, values)
db.commit()
# 关闭游标和数据库连接
cursor.close()
db.close()
"""
redis
import redis
r = redis.Redis(
host='127.0.0.1',
port=6379,
password=""
)
r.set('foo', 'Bar')
print(r.get('foo'))
csv
读取csv文件内容
import csv
with open('example.csv', 'r') as file:
reader = csv.reader(file)
for row in reader:
print(row)
写入csv文件内容
import csv
data = [
['Alice', 30, 'New York'],
['Bob', 25, 'Los Angeles']
]
with open('example.csv', 'w') as file:
writer = csv.writer(file)
writer.writerow(['Name', 'Age', 'City'])
writer.writerow(['John', '21', 'Shang Hai'])
writer.writerows(data)
pandas 读取csv文件
import pandas
data = pandas.read_csv("example.csv")
print(data)
numpy
# init
x = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4])
x = np.arange(1, 7) # [1 2 3 4 5 6]
x = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])
z = x.reshape(6) # [1 2 3 4 5 6]
# add
x = np.append(x, 0)
x = np.append(x, [6, 7, 5])
# sort
x = np.sort(x)
print(x.sum())
print(np.mean(x))
print(np.median(x))
print(np.var(x))
print(np.std(x))
pandas
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index = ["James", "Bob", "Amy", "Dave"])
print(df)
print(df["ages"])
print(df[["ages", "heights"]])
print(df.loc["Bob"])
print(df.iloc[2])
print(df.iloc[:3])
print(df[(df["ages"] > 18) & (df["heights"] > 180)])
# csv
df = pd.read_csv("ca-covid.csv")
df.set_index("date", inplace=True)
df.drop("state", axis=1, inplace=True)
df["month"] = pd.to_datetime(df["date"], format="%d.%m.%y").dt.month_name()
print(df)
print(df.head())
print(df.info())
print(df.describe())
print(df["month"].value_counts())
print(df["cases"].sum())
print(df.groupby("month")["cases"].sum())
selenium
网页自动化库
安装
$ pip install selenium
Usage
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys
import time
# step 1: 声明浏览器
driver = webdriver.Chrome()
driver = webdriver.Safari()
driver = webdriver.Edge()
driver = webdriver.Firefox()
driver = webdriver.PhantomaJS() # 无界面浏览器, 获取的截图是长图,一般浏览器为可见截图
# step 2: 打开网页
driver.get("https://www.baidu.com")
# step 3: 定位元素
driver.find_element(by=By.ID, value="message") # id = #message
driver.find_element(by=By.CLASS_NAME, value="box") # class = .box
driver.find_element(by=By.CSS_SELECTOR, value="button") # <button></button>
# step 4: 操作元素
.click()
.send_keys("hello world", Keys.ENTER)
.text
.get_attribute('href')
driver.find_element(by=By.ID, value="message").send_keys("hello world")
driver.find_element(by=By.ID, value="message").click()
driver.find_element(by=By.ID, value="message").clear()
driver.find_element(by=By.ID, value="message").submit()
# step 5: 等待响应
driver.implicitly_wait(5) # 隐式等待,最长5s
time.sleep(random.randint(1, 2))
time.sleep(3) # 强制等待
# step 6: 常用方法
driver.save_screenshot('*.png') # 截图
driver.back() # 返回上一页
driver.forward() # 返回下一页
driver.refresh() # 刷新页面
driver.close() # 关闭当前页面窗口
driver.quit() # 关闭浏览器
driver.maximize_window() # 最大化窗口
driver.set_window_size(900, 500) # 设置窗口大小
# 关闭浏览器
driver.quit()
other
#不显示浏览器操作,只显示结果,后台运行
from selenium.webdriver.chrome.option import Options
opt = Options()
opt.add_argument("--headless")
opt.add_argument("--disable-gpu")
driver = webdriver.Chrome(options=opt)
from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys
.send_keys(Keys.ENTER) # enter
.send_keys(Keys.TAB) # tab
.send_keys(Keys.SPACE) # space
.send_keys(Keys.ESCAPE) # esc
.send_keys(Keys.BACKSPACE) # 删除x
.send_keys(Keys.CONTROL, 'a') # 全选
.send_keys(Keys.CONTROL, 'c') # 复制
.send_keys(Keys.CONTROL, 'v') # 粘贴
.send_keys(Keys.CONTROL, 'x') # 剪切
.send_keys(Keys.CONTROL, 'z') # 撤销
example
from selenium import webdriver
url = "https://movie.douban.com/chart"
# 初始化
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
# 打开网页
browser.get(url)
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys
# 查找元素
web.find_element(By.ID, 'key')
# 定位元素并按键操作
elem = web.find_element(By.ID, 'key') # 定位到搜索框
elem.send_keys("口罩") # 模拟键盘输入关键字
elem.send_keys(Keys.ENTER) # 模拟键盘按Enter键
elem.text # 获取文本内容
elem.click() # 模拟鼠标点击
elem.send_keys(Keys.ENTER)
web.back() # 返回上一页
web.forward() # 前往下一页
web.refresh() # 刷新页面
web.quit() # 关闭浏览器
web.close() # 关闭当前窗口
pyautogui
import pyautogui as pg
# 屏幕操作
pg.size() # 获取屏幕分辨率
pg.position() # 获取当前鼠标位置
pg.screenshot() # 截屏
pg.locateOnScreen() # 查找图片位置,图片识别
pg.locateCenterOnScreen('*.png') # 查找图片中心位置
pg.locateCenterOnScreen('*.png', grayscale=False, confidence=0.7)
# pip install opencv-python
# 截图
pg.screenshot(path) # 全图截屏
pg.screenshot('01.png',region=(0,0,300,400)) # 区域截屏(左上角坐标,宽,高)
# 鼠标移动
pg.moveTo(100, 100) # 移动到指定位置
pg.move(x, y) # 移动相对位置
# 鼠标点击
pg.click() # 鼠标点击当前位置,默认左键点击
pg.rightClick() # 单击右键
pg.middleClick() # 单击中键
pg.doubleClick() # 双击鼠标左键
pg.tripleClick() # 三连击
pg.click(x, y, duration=2) # 鼠标点击指定坐标,duration为点击间隔时间
pg.click(button='right') # 鼠标右键点击当前位置
pg.click(clicks=6, interval=0.4) # 多次连击
pg.click(pg.locateCenterOnScreen('*.png')) # 图片定位再点击
# 鼠标拖动
pg.dragTo(x, y) # 拖动
pg.dragRel() # 拖动相对位置
# 鼠标滚动
pg.scroll() # 滚动
# 键盘按下和释放
pg.press() # 按下并松开
pg.keyDown() # 按住
pg.keyUp() # 松开
# 键盘输入文本
pg.typewrite("Hello, world!") # 模拟键盘输
pg.write('hello python !', interval=0.3) # 控制键盘输入,interval间隔输入字符时间
# 键盘组合键
pg.hotkey("ctrl", "c") # 模拟组合键操作
# 弹窗
pg.alert(text='是否确认运行程序’, title='请求框', button='OK') # 消息提醒框
pg.confirm(text='welcome to my world !', title='WeChat', buttons=['OK', 'Cancel']) # 选择框
pg.prompt(text='请输入您的开机密码', title='输入框', default='0627***') # 内容输入框(可看到输入的内容)
pg.password(text='开机密码', title='消息框',default='密码', mask='*') # 密码输入框(隐藏输入的内容)
