Rust
Getting Start
Install
# install rustup
$ curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh
$ source "$HOME/.cargo/env"
$ rustc --version # -V
# rustc 1.63.0
$ cargo --version # -V
# cargo 1.63.0
cargo new 创建rust项目
$ cargo new rust-hello
$ cd rust-hello
$ cargo run
# Compiling rust-hello v0.1.0 (/Users/coulsonzero/Downloads/rust-hello)
# Finished dev [unoptimized + debuginfo] target(s) in 0.42s
# Running `target/debug/rust-hello`
Hello, world!
编译器 Clion
Overview
Hello World
fn main() {
println!("hello world!");
}
Variables & Constant
- let
- const
- static
// let 绑定变量
let x: i32 = 12; // 不可变变量
let mut y: i32 = 20; // 可变变量 mut
// let shadowing 特性
let x: i32 = 12;
let x: f64 = 3.14;
let x: char = 'k';
let x: &str = "John Smith";
// assign multiple vars
let (name, age) = ("John Smith", 21);
// const 常量
const PI: f64 = 3.14159;
// static 静态全局变量,操作修改需使用unsafe
static mut z: i32 = 0;
unsafe {
z += 1;
println!("{}", z);
}
let: 绑定变量, 可以给同一个变量绑定不同值, 但使用的内存地址不同 (eg: 相同的人管理不同的事务)
let可以省略大于2个字符的类型,但不推荐
mut:使变量值可以改变
const:常量
static:静态变量,指向同一个堆内存地址, 操作修改需使用unsafe使内存安全
Output
println!("hello, world!");
// format
println!("hello {}", "John Smith");
println!("{1} is located in {2}, and my name is {0}, ", "John Smith", "Shanghai", "China");
println!("{city} is located in {country}", city = "Shanghai", country = "China");
println!("Binary: {:b} Hex: {:x} Octal: {:o}", 10, 10, 10);
println!("{:?}", (12, true, "hello")); // (12, true, "hello")
Input
// input a line string:
let mut s = String::new();
io::stdin().read_line(&mut s).expect("error");
println!("{}", s)
// input a number:
// --snip--
println!("Please enter a Number: ");
let mut s = String::new();
io::stdin().read_line(&mut s).expect("error");
let num: u32 = s.trim().parse().expect("error");
println!("{}", num)
Data Type
- Number:
- Int(
默认:i32) :i8, i16, i32, i64, i128, isizeu8, u16, u32, u64, u128, usiz
- Float(
默认: f64):f32, f64
- Int(
- Bool:
bool - Char:
char - String:
&str,String
let x: i32 = 12;
let x: f64 = 10.6;
let x: bool = true;
let x: char = 'k';
let x: &str = "John Smith";
let x: String = String::from("hello world");
// array
let x: [i32; 5] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
// tuple
let x: (i32, f64, u8) = (500, 6.4, 1);
// vector
let mut nums: Vec<i32> = vec![1, 2, 3, 4];
// hashmap
let mut map = HashMap::new();
// variable address
println("{:p}", &x);
type_of(&nums); // [i32; 6]
type_of(&[-5, 4, 1, 32, -3, 2]); // [i32; 6]
type_of(&32.90); // prints "f64"
type_of(&vec![1, 2, 4]); // prints "std::vec::Vec<i32>"
type_of(&"foo"); // prints "&str"
fn type_of<T>(_: &T) {
println!("{}", std::any::type_name::<T>() );
}
Comment
// single comment
/*
* multi-line comment
*/
/// document comment (method header)
///
/// Use [`eprint!`] instead to print error and progress messages.
///
/// necessary to use [`io::stdout().flush()`][flush] to ensure the output is emitted
/// immediately.
///
/// using the `Debug` implementation
///
/// # Examples
///
/// ```rust
/// use std::io::{self, Write};
///
/// print!("this string has a newline, why not choose println! instead?\n");
///
/// io::stdout().flush().unwrap();
/// ```
//! document comment (file header)
//!
//! ```
//! (1) string:
//! a) for c in s.chars() {...}
//! b) for (_, c) in s.chars().enumerate() {...}
//! (2) array:
//! for v in nums {...}
//! ```
for example
/* ================ main.rs ================ */
#![allow(dead_code)] // warning: struct `Rectangle` is never constructed, warning: function `run` is never used
#![allow(unused_imports)] // unused import: `crate::template::template_impl as ti`
#![allow(unused_variables)] // unused variable: `integer`
//! simplify the usage of module
// use add::add_one::plus;
// use crate::basic::output;
// use crate::basic::datatype;
// use crate::basic::vars;
// use crate::control::while_loop;
// use crate::core::string;
// use crate::core::tuple;
// use crate::core::vector;
// use crate::core::hashmap;
// use crate::template::template_func as tf;
// use crate::template::template_struct as ts;
use crate::template::template_impl as ti;
use crate::template::template_impl_2 as ti2;
// use crate::structs::struct_impl_for as sif;
/// manage modules
// mod add;
// mod basic;
// pub mod control;
// mod core;
mod template;
// mod functions;
mod structs;
mod macros;
// mod depends;
/// note: `#[warn(dead_code)]` on by default
fn main() {
/* module usage example */
// println!("{}", plus(1));
/* basic */
// output::run();
// datatype::run();
// vars::run();
// basic::vars_more::run();
// basic::vars_more::let_example();
/* control */
// control::for_loop::run();
// while_loop::run();
/* core */
// string::hi("John Smith".to_string());
// string::run();
// tuple::run();
// vector::run();
// hashmap::run();
// core::str::run();
/* functions */
// functions::fun::run();
// functions::rand::run();
// structs
// structs::struct_func::run();
// structs::struct_impl::run();
// sif::run();
/* template */
// tf::run();
// ts::run();
// ti::run();
// ti2::run();
/* macros */
// macros::macro_r::run();
// macros::type_of::example();
// macros::color::example();
macros::color::example();
/* depends */
// depends::depend::run();
}
// output:
Control & Loop
If statement
if condition {
// statement(s)
} else if condition {
// statement(s)
} else if condition {
// statement(s)
} else {
// statement(s)
}
/// a > b ? a : b
let res = if a > b {a} else {b};
return if a > b {a} else {b};
Match statement
let day: i32 = 3;
let res = match day {
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 => "Workday",
6 => "Saturday",
7 => "Sunday",
_ => "default",
};
println!("{:?}", res); // Workday
let day: i32 = 3;
println!("{:?}", match day {
1..=5 => "Workday",
6 => "Saturday",
7 => "Sunday",
_ => "default",
});
#[test]
fn test_char() {
let c = '2';
let res: &str = match c {
'1'..='9' => "integer",
'a'..='z' => "lower letter",
'A'..='Z' => "upper letter",
_ => "default",
};
println!("{:?}", res);
}
for loop
// (1) str || string:
a) for c in s.chars() {...}
b) for (_, c) in s.chars().enumerate() {...}
// (2) array || vector:
for i in 0..nums.len() {} // set or get
for v in nums {} // get
for v in nums.iter() {} // get
for v in &mut nums {} // set or get
for v in nums.iter_mut() {} // set or get
// (3) hashmap:
for (k, v) in &map {}
example
// &str || String
pub fn for_str(s: &str) {
print!("|\x1b[96m{:?}\x1b[0m| => {{ ", s);
for (_, c) in s.chars().enumerate() {
print!("{:?} ", c);
}
println!("}}");
}
// array || vector
pub fn for_array(nums: &mut [i32]) {
print!("|\x1b[96m{:?}\x1b[0m| => ", nums);
print!("[ ");
for i in 0..nums.len() {
print!("{}", nums[i]);
if i != nums.len()-1 {
print!(", ");
}
}
println!(" ]");
}
#[test]
pub fn test_for() {
for_str("hello world");
for_str(&String::from("hello world"));
// output: { 'h' 'e' 'l' 'l' 'o' ' ' 'w' 'o' 'r' 'l' 'd' }
let mut arr: [i32; 5] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
let mut vector: Vec<i32> = vec![1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
for_array(arr.as_mut());
for_array(vector.as_mut_slice());
// output: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
}
While loop
// Infinite loop
fn loop_example() {
let mut count: i32 = 0;
loop {
print!("{} ", count);
count += 1;
if count == 6 {break};
}
println!();
}
// 0 1 2 3 4 5
// While loop
fn while_loop_example() {
let mut count: i32 = 0;
while count < 6 {
print!("{} ", count);
count += 1;
}
println!();
}
// 0 1 2 3 4 5
fn for_range_example() {
// For Range
for x in 0..6 {
print!("{} ", x);
}
println!();
}
// 0 1 2 3 4 5
Core
str
字符串切片, 由长度和指针构成
// &str 是String 的切片类型。
let s: &str = "hello";
println!("{}", s.len()); // len : 5
println!("{:?}", s.as_bytes()); // bytes: [104, 101, 108, 108, 111]
println!("{:p}", s.as_ptr()); // ptr : 0x1026b6760
println!("{:p}", &s); // &s : 0x16dce2f08
println!("{}", s.is_empty()); // false
println!("{}", s.clone()); // hello
println!("{}", s.repeat(2)); // hellohello
println!("{}", s.to_lowercase()); // hellohello
println!("{:?}", s.to_uppercase()); // "HELLO"
for example
fn main() {
println!("{}", hi("John Smith"));
}
// &str 传值
fn hi(name: &str) -> String {
return "hi ".to_string() + name;
}
&str - String
fn main() {
let first_name: &str = "Pascal";
let last_name: String = "John Smith".to_string();
greet(first_name);
greet(&last_name); // `last_name` is passed by reference
}
fn greet(name: &str) {
println!("Hello, {}!", name);
}
String
长度、容量和指针构成
// init
let s: &str = "Hello, world!";
let s: String = String::from("Hello, world!");
let s: String = "Hello, world!".to_string();
let s: String = "Hello, world!".into();
let s = String::new();
// methods
s.len() -> usize
s.capacity() -> usize
s.push(e: char)
s.push_str(ss: String)
s.insert(i: i32, e: char)
s.pop()
s.clear()
// iter
for c in s.chars() {
print!("{}", c);
}
println!();
// iter-enum
for (_, v) in s.chars().enumerate() {
print!("{}", v);
}
println!();
Array
/// init array
let nums = [-5, 4, 1, 32, -3, 2];
let mut nums = [-5, 4, 1, 32, -3, 2];
let mut nums: [i32; 5] = [-5, 4, 1, 32, -3, 2];
// init vector
let nums = vec![-5, 4, 1, 32, -3, 2];
let mut nums = vec![-5, 4, 1, 32, -3, 2];
let mut nums: Vec<i32> = vec![-5, 4, 1, 32, -3, 2];
println!("{:?}", nums);
println!("{:?}", nums.to_vec()); // array -> vector
// for loop
for i in 0..nums.len() {
// get: print!("{} ", nums[i]);
// set: nums[i] += 1;
}
/// sort
nums.sort(); // [-5, -3, 1, 2, 4, 32]
nums.sort_by(|a, b| a.cmp(b)); // [-5, -3, 1, 2, 4, 32]
/// reverse sort
nums.sort_by(|a, b| b.cmp(a)); // [32, 4, 2, 1, -3, -5]
/// sort by string
nums.sort_by_cached_key(|k| k.to_string()); // [-3, -5, 1, 2, 32, 4]
/// shuffle
use rand::prelude::*;
nums.shuffle(&mut rand::thread_rng()); // [4, -3, 2, -5, 32, 1]
array as params of funciton
pub fn for_array(nums: &mut [i32]) {
// --snip--
}
fn main() {
let mut arr: [i32; 5] = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
let mut vector: Vec<i32> = vec![1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
for_array(arr.as_mut());
for_array(vector.as_mut_slice());
}
Vector
// --init--
let mut nums = Vec::new();
let mut nums: Vec<i32> = Vec::new();
let nums = vec![1, 2, 3, 4];
let mut nums: Vec<i32> = vec![1,2,3,4];
let mut nums: Vec<i32> = (1..10).collect();
// --methods--
增:push(e)
删:pop()
查:nums[i], &nums[i], &nums[0..2]
改:nums[i] = v
长度:len()
打印:println!("nums: {:?}", nums);
Hashmap
// init
let mut map: HashMap<&str, i32> = HashMap::new();
let map = HashMap::from([("a", 1),("b", 2),("c", 3)]);
// methods
map.insert(k, v);
println!("{:?}", map);
// for-loop
for (k, v) in map {
println!("{}: {}", k, v);
}
Tuple
pub fn run () {
let x: (i32, f64, u8) = (500, 6.4, 1);
let a: i32 = x.0;
let b: f64 = x.1;
let c: u8 = x.2;
println!("{:?}", (a, b, c));
}
OOP
Funciton
fn hello() {
println!("hello world!");
}
// hello("John Smith")
fn hello(name: &str) {
println!("hi ".to_string() + name);
}
// hey("John Smith".to_string())
fn hey(name: String) -> String {
return "hey ".to_string() + &name;
}
fn max(a: i32, b: i32) -> i32 {
return if a > b {a} else {b};
}
// let (a, b) = info("John Smith", 21)
fn info(name: &str, age: i32) -> (String, i32) {
return ("my name is ".to_string() + name, age);
}
Struct
// 1 struct: fields
struct Animal {
name: String,
age: i32
}
// 2 supper: to inherit the basic structure.
struct Animal {
name: String,
age: i32
}
struct Cat {
supper: Animal, /// inherit
type_name: i32
}
// 3 impl: methods
struct Rectangle {
width: u32,
height: u32,
}
impl Rectangle {
fn new(w: u32, h: u32) -> Rectangle {
return Rectangle { width: w, height: h };
}
fn area(&self) -> u32 {
return self.width * self.height
}
fn can_hold(&self, other: &Rectangle) -> bool {
self.width > other.width && self.height > other.height
}
fn square(size: u32) -> Self {
Self { width: size, height: size }
}
}
#[test]
fn test_impl() {
let rect1 = Rectangle {
// code
}
/// impl methods
println!("area: {} ", rect1.area());
let rect2 = Rectangle::new(20, 12);
println!("{} {}", rect.height, rect.width);
}
// trait: different structs use the same methods.
// a) trait_name::struct_name::impl_for_method();
// b) struct_ini.impl_for_method()
struct Tweet {
// code
}
struct NewsArticle {
// code
}
trait Summary {
fn summarize(&self) -> String;
}
impl Summary for Tweet {
fn summarize(&self) -> String {
// code
}
}
impl Summary for NewsArticle {
fn summarize(&self) -> String {
// code
}
}
#[test]
fn test_trait_summary() {
let tweet = Tweet {
// code
}
let article = NewsArtic
// code
}
println!("{}", article.summarize());
println!("{}", tweet.summarize());
/// use trait method;
println!("{}", Summary::summarize(&article));
println!("{}", Summary::summarize(&tweet));
}
Template
fn max<T: PartialOrd>(a: T, b: T) -> T {
return if a > b {a} else {b};
}
fn largest<T: PartialOrd>(list: &[T]) -> &T {
let mut largest = &list[0];
for item in list {
if item > largest {
largest = item;
}
}
return largest
}
#[test]
fn test_max() {
println!("{:?}", max(3, 7)); // 7
}
#[test]
fn test_largest() {
let vec_nums = vec![34, 50, 25, 100, 65];
let vec_char = vec!['y', 'm', 'a', 'q'];
println!("output: {:?}", largest(&vec_nums)); // 100
println!("output: {:?}", largest(&vec_char)); // 'y'
}
struct Point<X1, Y1> {
x: X1,
y: Y1,
}
impl<X1, Y1> Point<X1, Y1> {
fn new(x: X1, y: Y1) -> Point<X1, Y1> {
return Point { x, y}
}
fn mix<X2, Y2>(self, other: Point<X2, Y2>) -> Point<X1, Y2> {
return Point { x: self.x, y: other.y }
}
}
#[test]
fn test_struct_temp() {
let integer = Point { x: 5, y: 10 };
let float = Point { x: 1.0, y: 4.0 };
let int_float = Point { x: 5, y: 4.0 as i32 };
let p = Point { x: 5, y: 10 };
println!("point: ({}, {})", p.x, p.y); // point: (5, 10)
let p = Point::new(3, 6);
println!("point: ({}, {})", p.x, p.y); // point: (3, 6)
let p1 = Point::new(5, 10.4);
let p2 = Point::new("hello", 'c');
let p3 = p1.mix(p2);
println!("point: ({:?}, {:?})", p3.x, p3.y); // point: (5, 'c')
}
Macros
#[macro_export]
macro_rules! vector {
( $( $x:expr ),* ) => {
{
let mut temp_vec = Vec::new();
$(
temp_vec.push($x);
)*
temp_vec
}
};
}
#[macro_export]
macro_rules! hashmap {
($($key: expr => $val: expr), *) => {
{
let mut temp_map = std::collections::HashMap::new();
$(
temp_map.insert($key, $val);
)*
temp_map
}
};
}
pub fn type_name<T>(_: T) -> &'static str {
std::any::type_name::<T>()
}
#[macro_export]
macro_rules! type_of {
() => {
eprintln!("[{}, {}]", file!(), line!());
};
($val:expr) => (
eprintln!("[\x1b[92m{}\x1b[0m, {}], \x1b[93m${:14}\x1b[0m: {}",
file!(), line!(), stringify!($val), type_name($val)
);
);
}
#[test]
fn test_vector() {
let v = vector![1, 2, 3];
assert_eq!(v, [1, 2, 3]);
}
#[test]
fn test_hashmap() {
let map = hashmap!(1 => "one", 2 => "two", 3 => "three" );
println!("map {:?} ",map);
}
// map {2: "two", 3: "three", 1: "one"}
#[test]
fn test_typeof() {
println!("{}", type_name(32)); // i32
println!("{}", type_name(3.14)); // f64
println!("{}", type_name(false)); // bool
println!("{}", type_name('k')); // char
println!("{}", type_name("hello")); // &str
println!("{}", type_name([1,3, 5])); // [i32; 3]
println!("{}", type_name(vec![1,3, 5])); // alloc::vec::Vec<i32>
type_of!(); // [src/main.rs, 27]
type_of!(12); // [src/main.rs, 28] $12 : i32
type_of!(vec![1, 3, 5]); // [src/main.rs, 29] $vec![1, 3, 5] : alloc::vec::Vec<i32>
}
Cargo
$ cargo new rust-hello
$ cargo build
$ cargo run
$ cargo update
cargo build
# debug(调试)模式(默认)
# 编译时间较短,因为编译器不进行优化,但代码运行速度较慢
$ cargo build
# 将结果二进制文件放入target/release,而不再是target/debug目录
# 发布(release)模式编译需要更长时间,但代码运行速度更快
$ cargo build --release
cargo test
使用本项目测试
$ tree .
.
├── Cargo.lock
├── Cargo.toml
├── src
│ ├── plus.rs
│ ├── int_rle.rs
| |── macros
| | └── vector.rs
│ └── lib.rs
└── tests
└── test_plus.rs
# Cargo.toml
[package]
name = "rust_lib"
version = "0.1.0"
edition = "2021"
# See more keys and their definitions at https://doc.rust-lang.org/cargo/reference/manifest.html
[dependencies]
// src/lib.rs
pub mod plus;
pub mod int_rle;
pub mod macros;
// plus.rs
pub fn add(left: usize, right: usize) -> usize {
left + right
}
// int_rle.rs
#[derive(Debug, PartialEq)]
pub struct IntRle {
pub values: Vec<i32>,
}
// src/macros/vector.rs
#[macro_export]
macro_rules! vector {
($($x:expr), *) => {
{
let mut temp_vec = Vec::new();
$(
temp_vec.push($x);
)*
temp_vec
}
};
}
pub fn example() {
let v = vector![1, 2, 3];
println!("vec {:?}", v);
}
/* tests/test_plus.rs */
extern crate rust_lib;
pub use rust_lib::*;
#[cfg(test)]
mod tests {
#[test]
fn it_works() {
let res = super::plus::add(2, 2);
assert_eq!(res, 4);
}
#[test]
fn test_int_rle() {
super::int_rle::IntRle { values: vec![1, 2, 3] };
}
#[test]
fn test_macros_vector() {
super::macros::vector::example();
}
}
$ cargo test
# cargo test -doc
# running 3 tests
# test tests::it_works ... ok
# test tests::test_int_rle ... ok
# test tests::test_macros_vector... ok
# test result: ok. 3 passed; 0 failed; 0 ignored; 0 measured; 0 filtered out; finished in 0.00s
cargo update
$ cargo update # updates all dependencies
$ cargo update -p rand # updates just “rand”
Cargo.toml
- step-1
[dependencies]
time = "0.1.12"
regex = "0.1.41"
- step-2
$ cargo build
# cargo run
重新运行cargo build,Cargo 将获取新的依赖项及其所有依赖项,将它们全部编译,然后更新Cargo.lock
- step-3: 调用第三方库
extern crate regex;
use regex::Regex;
fn example() {
let re = Regex::new(r"^\d{4}-\d{2}-\d{2}$").unwrap();
println!("Did our date match? {}", re.is_match("2014-01-01"));
}
Cargo.lock
可删除,cargo run / cargo build会重新编译该文件
target
可删除,编译文件存放于此, cargo run / cargo build会重新编译该文件
FAQ
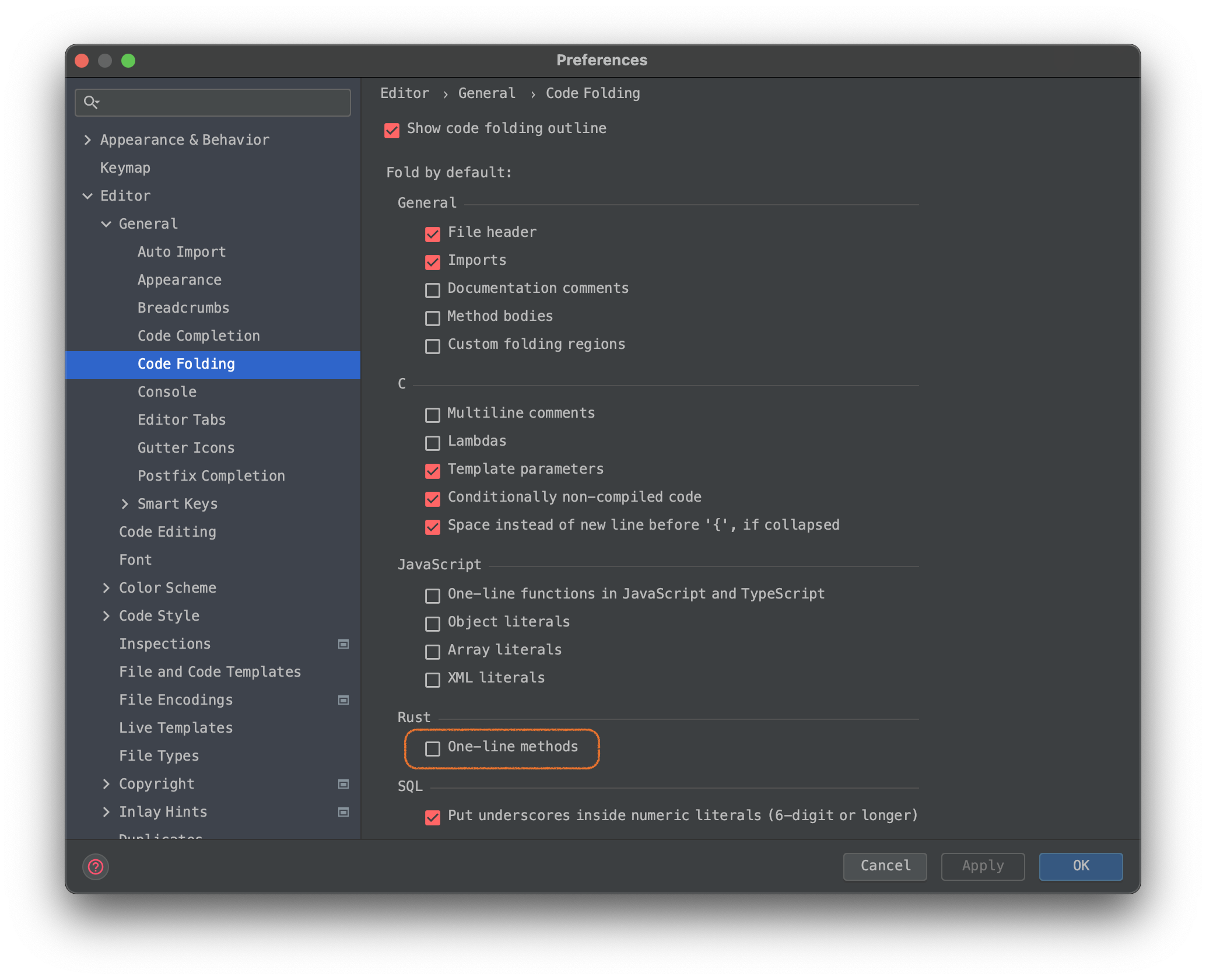
取消rust代码折叠
step-1: clion-preference
step-2: Editor-General-Code Folding-`Rust`--`One line method`
step-3: 取消勾选-apply即可
rustup
$ rustup --version # rustup -V
$ rustup update
$ rustup self uninstall
cargo
$ cargo --version
$ cargo new rust-hello
$ cargo build
$ cargo run
$ cargo test
$ cargo check
color
pub fn example() {
println!("\x1b[90m{}\x1b[0m", "[Error]: not found the function."); // 90: grey
println!("\x1b[91m{}\x1b[0m", "[Error]: not found the function."); // 91: red
println!("\x1b[92m{}\x1b[0m", "[Error]: not found the function."); // 92: green
println!("\x1b[93m{}\x1b[0m", "[Error]: not found the function."); // 93: yellow
println!("\x1b[94m{}\x1b[0m", "[Error]: not found the function."); // 94: blue
println!("\x1b[95m{}\x1b[0m", "[Error]: not found the function."); // 95: purple
println!("\x1b[96m{}\x1b[0m", "[Error]: not found the function."); // 96: cyan
println!("\x1b[97m{}\x1b[0m", "[Error]: not found the function."); // 97: white
println!("\x1b[98m{}\x1b[0m", "[Error]: not found the function."); // 98: light white (normal)
}
