MySQL
Overview
简介
SQL: Structured Query Language. 关系数据库语言的国际标准.
MySQL: a program that understands SQL. 市场上第一个开源关系型数据库软件
MySQL下载网址:
数据库分类
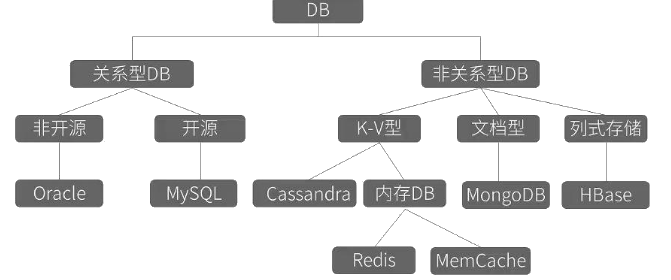
SQL分类
- DDL:数据定义语言 ,定义库、表、列等(CREATE、ALTER、DROP)
- DML:数据操作语言 ,操作数据库中表里的数据 (INSERT、UPDATE、DELETE)
- DCL:数据控制语言, 控制访问权限和安全级别 (GRANT、DENY)
- DQL:数据查询语言 (SELECT)
数据库的数据类型
- 整数
- int
- TINYINT
- SMALLINT
- MEDIUMINT
- BIGINT
- 浮点数和定点数(M::最大长度,D:小数位数)
- float(M,D)
- double(M,D)
- DECIMAL (M,D)
- 字符串
- varchar(M)
- CHAR(M)
- 文本
- TEXT
- TINYTEXT
- MEDIUMETEXT
- LONGTEXT
- 日期和时间
- YEAR
- DATE
- TIME
- DATATIME
- TIMESTAMP
- 二进制
- BLOB
- TINYBLOB
- MEDIUMBLOB
- LONGBLOB
数据库的基本操作
- 查询:show databases;
- 新建:creat database 数据库名;
- 删除:drop database 数据库名;
- 切换:use 数据库名;
- 新建并查看:show creat database 数据库名;
- 查看当前使用的数据库:select database();
数据表的基本操作:
- 查看:
showtables; - 创建:
creattable 表名(字段1 字段类型, 字段2 字段类型, ...); - 删除:
droptable 表名; - 新建并查看:show creat table 表名;
- 修改表名:alter table 表名
rename to新表名; - 合并表列from ... join ... on ...
- inner join
- left outer join
- right outer join
字段的基本操作:
- 查看字段:desc 表名;
- 增加字段:alter table 表名
add新增字段名 字段类型; - 删除字段:alter table 表名
drop字段名; - 修改字段:alter table 表名
change字段名 新字段名 字段类型;
数据表的约束:
- 主键约束:字段名 数据类型 promary key; primary key(字段名)
- 非空约束:字段名 数据类型 NOT NULL;
- 默认值约束:字段名 数据类型 default 默认值;
- 唯一性约束:字段名 数据类型 unique;
- 外键约束:...
下载 mysql 程序
查看 mysql 版本
方式一:linux 命令查询
$ mysql --version;
# mysql Ver 8.0.27 for macos11 on arm64 (MySQL Community Server - GPL)
$ mysql -V;
# mysql Ver 8.0.27 for macos11 on arm64 (MySQL Community Server - GPL)
方式二:mysql 内查询
mysql> select version();
# +-----------+
# | version() |
# +-----------+
# | 8.0.27 |
# +-----------+
# 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
MacOS 启动 mysql
# 启动 mysql
$ mysql -u root -p
# Enter password: ****
# 退出 mysql
mysql> exit
# Bye
Windows 运行 MySQL
以管理员权限运行CMD: Win+R -> 'cmd', 按ctrl+shift+enter
1. net start mysql
2. mysql -u root -p
Enter password:
3. ...
4. mysql> exit
5. net stop mysql (有时不用输入这个)
查看mysql版本
select version();
mysql --version;
mysql -V;
注释
# 单行注释
-- 单行注释
/* 多行注释 */
Database
SQL 查询数据库
-- 查询所有数据库
mysql> show databases;
-- 查询当前所在数据库名
mysql> select database();
SQL 使用数据库
-- use 数据库名;
use sql_hello;
SQL 新建数据库
-- create dabatase 数据库名;
create database sql_hello;
-- no error safe!
create database if not exists sql_hello;
SQL 删除数据库
-- drop database 数据库名;
drop database sql_hello;
-- no error safe!
drop database if exists sql_hello;
Table
SQL 查询表
- 查所有表名
show tables;
- 查表的创建结构(字段)
-- desc 表名;
desc users;
- 查表的数据内容
-- select 字段 from 表名;
select * from users;
example
mysql> show tables;
-- +---------------------+
-- | Tables_in_sql_hello |
-- +---------------------+
-- | users |
-- +---------------------+
-- 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> desc users;
+------------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+------------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| user_id | int | YES | | NULL | |
| first_name | varchar(100) | YES | | NULL | |
| last_name | varchar(100) | YES | | NULL | |
| city | varchar(100) | YES | | NULL | |
+------------+--------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
-- 4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from users;
-- Empty set (0.00 sec)
SQL 新建表
drop table if exists table_name;
create table if not exists table_name (
column1 datatype(size) AUTO_INCREMENT,
column2 datatype(size),
...
column3 datatype(size),
PRIMARY KEY(ID)
) ENGINE=InnoDB CHARAULT=utf8;
-- 约束
PRIMARY KEY:指定列,更快创建唯一索引来访问表
AUTO_INCREMENT: 自动递增,允许当新记录插入到表中时,生成一个唯一的编号
NOT NULL: 不能包含NULL值
DEFAULT:如果没有提供值的列。则该列获取设置的默认值,NULL
UNIQUE:不允许插入一列中重复的值,允许多个UNIQUE列
CHECK:检查该值是否有效
for example
create table users (
id int not null auto_increment,
username varchar(40) not null,
password varchar(40) not null,
primary key(id)
);
Example
drop table if exists employees;
create table employees (
id int not null auto_increment,
username varchar(100) not null,
password varchar(100) not null,
salary double,
primary key(id),
);
Example
-- int|varchar(size)|date
-- PRIMARY KEY|NOT NULL|AUTO_INCREMENT|UNIQUE|CHECK|DEFAULT
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS 'employees';
create table 'Users'(
'id' int(10) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
'username' varchar(30) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '用户名',
'password' varchar(20) NOT NULL DEFAULT '' COMMENT '用户密码',
'class' char(1) NOT NULL COMMENT '级别',
'hire_date' date NOT NULL COMMENT '上岗时间',
PRIMARY KEY('id')
) ENGINE=InnoDB CHARAULT=utf8 COMMENT='员工信息';
SQL 删除表
- 完全删除表(可回滚)
-- drop table [if exists] 表名;
drop table users;
drop table if exists users;
- 清空表数据,仅保留字段结构
-- truncate table 表名;
truncate table users;
- 删除表数据
-- delete from 表名 where ...
delete from users;
delete from users where user_id = 1;
异同
- truncate和delete 只删除数据不删除表结构
- truncate 删除后将
重建索引(新插入数据后id从0开始记起), - delete
不会删除索引(新插入的数据将在删除数据的索引后继续增加), - drop语句将删除表的结构包括依赖的约束,触发器,索引等;
- truncate 删除后将
- 安全性:drop和truncate删除时不记录MySQL日志,不能回滚,delete删除会记录MySQL日志,可以回滚;
- 返回值:delete 操作后返回删除的记录数,而 truncate 返回的是0或者-1(成功则返回0,失败返回-1);
用法
- 希望删除表结构时,用 drop;
- 希望保留表结构,但要删除所有记录时, 用 truncate;
- 希望保留表结构,但要删除部分记录时, 用 delete。
SQL 修改表
-- alter table ... rename as ...;
alter table users rename as employees;
-- rename table 旧的表名 to 新的表名;
rename table users to employees;
复制表
同时复制表内容和结构
CREATE TABLE new_table SELECT * FROM new_table;
复制表内容
INSERT INTO new_table SELECT * FROM new_table;
复制表结构
CREATE TABLE new_table LIKE new_table;
表连接
select t1.*, t2.* from table1 [as] t1, table2 [as] t2 where t1.id = t2.id;
SELECT column_name(s) FROM t1 [INNER|LEFT|RIGHT] JOIN t2 ON t1.column_name=table2.column_name;
select Name,City from customers union select Name,Customer_ID from orders;
Data
SQL 新增表格数据
-- 插入单条数据
insert [ignore] into 表名 values(value1, value2); -- 值数量与行数量需一致 ignore:如果数据已经存在,请忽略
insert [ignore] into 表名(字段1,字段2) values(value1, value2); -- 可特定数量,sql插入会自动排序
-- 批量插入数据
insert [ignore] into 表名(字段1,字段2) values
(value1, value2),
(value1, value2),
...;
insert into table_name values(...);
insert into 表名 values
(...),
(...),
(...);
for example
CREATE TABLE leaderboard (
place int,
nickname varchar(128),
rating int,
PRIMARY KEY(place)
);
INSERT INTO leaderboard VALUES
(1, 'Predator', 9500),
(2, 'JohnWar', 9300),
(3, 'NightWarrior', 8900);
-- 批量插入数据
insert into actor values
(1, 'PENELOPE','GUINESS', '2006-02-15 12:34:33'),
(2, 'NICK', 'WAHLBERG', '2006-02-15 12:34:33');
SQL 删除表格数据
-- delete from 表名 where ...;
delete from leaderboard where place = 1;
delete from leaderboard;
-- truncate table 表名;
drop table if exists employees;
create table employees (
id int not null auto_increment,
username varchar(100) not null,
password varchar(100) not null,
salary double,
primary key(id),
);
insert into employees(username, password, salary) values
('john', 'admin123', 76289),
('tom', '123456', 19900),
('koul', 'tuiok145', 39870);
---------------------------------------------------------
-- mysql> select * from employees;
-- +----+----------+----------+--------+
-- | id | username | password | salary |
-- +----+----------+----------+--------+
-- | 1 | john | admin123 | 76289 |
-- | 2 | tom | 123456 | 19900 |
-- | 3 | koul | tuiok145 | 39870 |
-- +----+----------+----------+--------+
mysql> delete from employees;
mysql> insert into employees(username, password, salary) values
-> ('john', 'admin123', 76289),
-> ('tom', '123456', 19900),
-> ('koul', 'tuiok145', 39870);
-- mysql> select * from employees;
-- +----+----------+----------+--------+
-- | id | username | password | salary |
-- +----+----------+----------+--------+
-- | 4 | john | admin123 | 76289 |
-- | 5 | tom | 123456 | 19900 |
-- | 6 | koul | tuiok145 | 39870 |
-- +----+----------+----------+--------+
mysql> truncate table employees;
mysql> insert into employees(username, password, salary) values
-> ('john', 'admin123', 76289),
-> ('tom', '123456', 19900),
-> ('koul', 'tuiok145', 39870);
mysql> select * from employees;
-- +----+----------+----------+--------+
-- | id | username | password | salary |
-- +----+----------+----------+--------+
-- | 1 | john | admin123 | 76289 |
-- | 2 | tom | 123456 | 19900 |
-- | 3 | koul | tuiok145 | 39870 |
-- +----+----------+----------+--------+
SQL 查询表格数据
select 字段名 from 表名 where ...;
select [distinct] 查询列表 [As 新名] from 表名
[[inner/left/full out] join ... on ...]
[where ...]
[group by ...]
[order by ... [desc|asc]];
-- union: 连接两个select
-- 查询列表可以是:表中的字段、常量值、表达式、函数
-- 例如: select id,name/* from user;
-- distinct: 去重
-- As:重命名
where筛选
-- where sex='man'; where age>=18 and age <=24;
-- 条件运算符:= != > < >= <= <>
-- 逻辑运算符:and or not()
-- 模糊查询:like ...、between ... and ...、 in() 、is [not] null
-- like '%a_' : %匹配多个,_匹配一个字符 /_转义:表示_不作为通配符
-- between .. and ...: where age>=18 and age<=24; => where age between 18 and 24;
-- in: where sex in ('man', 'woman');
-- is null: where id is [not] null;
排序order by ... [desc|asc]
asc: 升序(默认)
desc: 降序
order by age desc;
order by salary*12*(1+ifnull(..., 0)) desc;
order by length(last_name) desc; //按名称长度降序
order by salary desc, employee_id asc; //多个字段排序:先按工资降序,再按employ_id升序
SQL 修改表格数据
-- update ... set ... where ...;
update `employees` set password = 'koul123', salary = 10000 where username = 'koul';
example
-- 将id=5以及emp_no=10001的行数据替换成id=5以及emp_no=10005,其他数据保持不变,使用replace实现,直接使用update会报错
update titles_test set emp_no = replace(emp_no, 10001, 10005) where id = 5;
Column
SQL 新增表格字段
-- single column
alter table employees add city varchar(100);
example
-- mutiple columns
alter table employees add (
country varchar(100),
sex varchar(30)
);
alter table employees
add country varchar(100),
add sex varchar(30)
;
-- 增加外键约束
alter table audit add constraint foreign key(emp_no) references employees_test(ID);
-- mysql> desc employees;
-- +----------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
-- | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
-- +----------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
-- | id | int | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
-- | username | varchar(100) | NO | | NULL | |
-- | password | varchar(100) | NO | | NULL | |
-- | salary | double | YES | | NULL | |
-- | city | varchar(100) | YES | | NULL | |
-- | country | varchar(100) | YES | | NULL | |
-- | sex | varchar(30) | YES | | NULL | |
-- +----------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
-- 7 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- mysql> select * from employees;
-- +----+----------+----------+--------+------+---------+------+
-- | id | username | password | salary | city | country | sex |
-- +----+----------+----------+--------+------+---------+------+
-- | 1 | john | admin123 | 76289 | NULL | NULL | NULL |
-- | 2 | tom | 123456 | 19900 | NULL | NULL | NULL |
-- | 3 | koul | koul456 | 20000 | NULL | NULL | NULL |
-- +----+----------+----------+--------+------+---------+------+
SQL 删除表格字段
-- drop single field
alter table employees drop city;
-- drop mutiple fields
alter table employees drop country, drop sex;
SQL 查询表格字段
-- desc 表名;
desc employees;
example
-- select * from employees;
-- mysql> desc employees;
-- +----------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
-- | Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
-- +----------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
-- | id | int | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
-- | username | varchar(100) | NO | | NULL | |
-- | password | varchar(100) | NO | | NULL | |
-- | salary | double | YES | | NULL | |
-- | city | varchar(100) | YES | | NULL | |
-- | country | varchar(100) | YES | | NULL | |
-- | sex | varchar(30) | YES | | NULL | |
-- +----------+--------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
-- mysql> select * from employees;
-- +----+----------+----------+--------+------+---------+------+
-- | id | username | password | salary | city | country | sex |
-- +----+----------+----------+--------+------+---------+------+
-- | 1 | john | admin123 | 76289 | NULL | NULL | NULL |
-- | 2 | tom | 123456 | 19900 | NULL | NULL | NULL |
-- | 3 | koul | koul456 | 20000 | NULL | NULL | NULL |
-- +----+----------+----------+--------+------+---------+------+
SQL 修改表格字段
- 修改字段名和字段类型: change
-- alter table 表名 change 旧的字段名 新的字段名 字段类型;
alter table employees change sex gender varchar(100);
example
alter table employees change sex gender char(1) comment '1: male, 0: famale';
-- muitple change
alter table employees
change sex gender char(1) comment '性别 , 1: 男, 2: 女',
change country countries varchar(100);
修改字段类型: modify
-- alter table 表名 modify 字段名 新的字段类型;
alter table employees modify gender varchar(60);
Index
新建索引
-- index
create index idx on employees(id);
-- unique index
create unique index idx_username on employees(username);
-- union index
create index idx_password_salary on employees(password, salary);
-- create [unique|fulltext|spatial] index ... on table_name(column_name);
-- Alter table ... add [unique] index ...(column_name);
-- creata table table_name (..., primary key(id), index index_name(title(5)));
- 创建表时新建索引
create table table_name (
...,
...,
primary key (id),
key idx_user_id (user_id)
);
create table table_name (
...,
index (column_name(size)),
unique index idx_username(username),
index idx_password_salary(password, salary),
fulltext index idx_gender(gender),
spatial index idx_salary(salary)
);
查询索引
-- show indexes from 表名称;
mysql> show index from employees;
-- +-----------+------------+---------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+---------+------------+
-- | Table | Non_unique | Key_name | Seq_in_index | Column_name | Collation | Cardinality | Sub_part | Packed | Null | Index_type | Comment | Index_comment | Visible | Expression |
-- +-----------+------------+---------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+---------+------------+
-- | employees | 0 | PRIMARY | 1 | id | A | 3 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | | YES | NULL |
-- | employees | 0 | idx_username | 1 | username | A | 3 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | | YES | NULL |
-- | employees | 1 | idx | 1 | id | A | 3 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | | YES | NULL |
-- | employees | 1 | idx_password_salary | 1 | password | A | 3 | NULL | NULL | | BTREE | | | YES | NULL |
-- | employees | 1 | idx_password_salary | 2 | salary | A | 3 | NULL | NULL | YES | BTREE | | | YES | NULL |
-- +-----------+------------+---------------------+--------------+-------------+-----------+-------------+----------+--------+------+------------+---------+---------------+---------+------------+
-- 5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
-- explain
mysql> explain select * from employees use index(idx) where username = 'tom';
-- +----+-------------+-----------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
-- | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
-- +----+-------------+-----------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
-- | 1 | SIMPLE | employees | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 33.33 | Using where |
-- +----+-------------+-----------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------------+
-- 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
删除索引
-- drop index index_name on table_name; (同表时索引不可同名)
-- alter table table_name drop index index_name;
-- alter table table_name drop primary key;
drop index idx_password_salary on employees;
alter table employees drop index idx_username;
索引优化原则
- 最左前缀法则:a->b->c 复合z没用a索引则bc也会失效
- 以下用法会导致索引失效
- 计算:如+-*/% is null 、is not null 、or !=
<> - 函数:sum(),round()等
- 手动/自动类型转换:id='1', 本来是数字,给写成字符串了
- 计算:如+-*/% is null 、is not null 、or !=
- 索引不要放在范围查询右边(范围之后的索引都失效,与B树有关)
- 避免select * 的使用
- like '%...'会失效=>like '...%'
- order by 使用了文件内排序,没有按照索引本身去做排序,在内存里开辟了新的空间,然后把数据复制了一份放到了空间里,在空间里进行排序,多占用内存空间,影响性能。将select * 改为select 具体行(覆盖索引),像order by字段可以不在mysql层面去做,可以通过java代码层面去做
- group by原理也是先排序后分组,where高于having
拓展
View
CREATE [OR REPLACE] VIEW view_name(...) AS SELECT column_name(s) FROM table_name [WHERE conditon];
SELECT * FROM view_name;
DROP VIEW view_name;
create view actor_name_view(first_name_v, last_name_v) as select first_name, last_name from actor;
筛选条件
WHERE condition
= != < <= > >=
AND OR NOT
BETWEEN IN LINK (多个AND用BETWEEN, 多个OR用IN)
WHERE ID = 7
WHERE city = 'New York'
WHERE (id = 1 OR id = 2) AND city = 'Boston'
WHERE column_name BETWEEN value1 AND value2
WHERE age BETWEEN 20 AND 35
WHERE column_name LIKE pattern
WHERE name LIKE 'A%'/'_oulson'
WHERE Salary > (SELECT AVG(salary) FROM employees)
WHERE name LIKE '%oulson' AND country IN(CN, USA)
LIMIT 4 // 前4个[1,4]
OFFSET 3 LIMIT 5 // [1,8]去掉前3个挑选后5个(starting from 4, show 5 results)
LIMIT 3, 5
-- 查询出现三次以上相同积分的情况
select number from grade group by number having count(*) >= 3;
-- 查询各个岗位分数的平均数,并且按照分数降序排序,结果保留小数点后面3位
select job,round(avg(score),3) as avg from grade by job order by score desc;
-- 查询在2025年内投递简历的岗位和数量,并且按数量降序排序
select job, sum(num) as cnt from resume_info where date between '2025-01-01' and '2025-12-31' group by job order by cnt desc;
Func
function():
count(): HAVING ...
concat(...): 拼接字符串
concat(name, ',' city)
group_concat(): 拼接一列为一行字符串
length(...):
char_length(): 字符长度
replace(column_name, old, new)
round(str,2): 结果保留小数点后2位
upper(...): 大写
lower()
format()
insert()
substr()
reverse()
repeat()
sum(...)
sqrt(...): 平方根
avg(...): 平均数
min(...)
max(...)
ifnull(): 将null设置为0
left(s, length) -- 返回字符串s的前n个字符
right(s, length) -- 右边n个字符
substr(s, start, length) -- s[-2:], 截取2个字符长度
substring(s, start) -- s[i:]
GROUP_CONCAT(emp_no): 汇总
-- string => float 保留2位小数
cast("3.14159" as decimal(10, 2))
convert("3.14159", decimal(10, 2))
DATE_FORMAT(CURDATE(), '%Y-%m-%d %r')
EXTRACT(type FROM d) 从日期 d 中获取指定的值,type 指定返回的值。type可为year,week,moth等等
CURDATE()
DATE()
DAY()
WEEK()
MONTH()
YEAR()
#2025年内的表达方法
where year(date) = 2025
where date like '2025%'
where date between '2025-01-01' and '2025-12-31’
SELECT id, name, score, dense_rank() over(ORDER BY score DESC) AS 'rank' FROM student;
row_number() over(ORDER BY score DESC) 123456
rank() over(ORDER BY score DESC) 113446
dense_rank() over(ORDER BY score DESC) 1223445
sum(salary) over(order by emp_no) 累进和
Not Exists
select * from employees
where not exists
(select emp_no from dept_emp where dept_emp.emp_no = employees.emp_no)
Case
select
date,
round(avg(type='no_completed'), 3) as p
-- round(sum(if(email.type='no_completed', 1, 0))/count(*), 3) as p
-- round(sum(case type when "completed" then 0 else 1 end)*1.0/count(type),3) as p
from email
where send_id in (select id from user where is_blacklist = 0)
and receive_id in (select id from user where is_blacklist = 0)
group by date
order by date;
explain ...;
ms级别
优化效果:硬件<系统配置<数据库表结构<SQL及索引
- select 具体行 > select *
- 存储引擎:engine=InnoDB charault=utf8
事务
构造一个触发器audit_log,在向employees_test表中插入一条数据的时候,触发插入相关的数据到audit中,然后从audit里面使用查询语句:
create trigger audit_log after insert on employees_test
for each row
begin
insert into audit values(new.ID,new.NAME);
end;
